The health of your gums is very important for your Oral health and general well-being. If you neglect your oral health, it can be affected and one common oral condition that affects many individuals is gum disease.
One may ask, why are gums important?
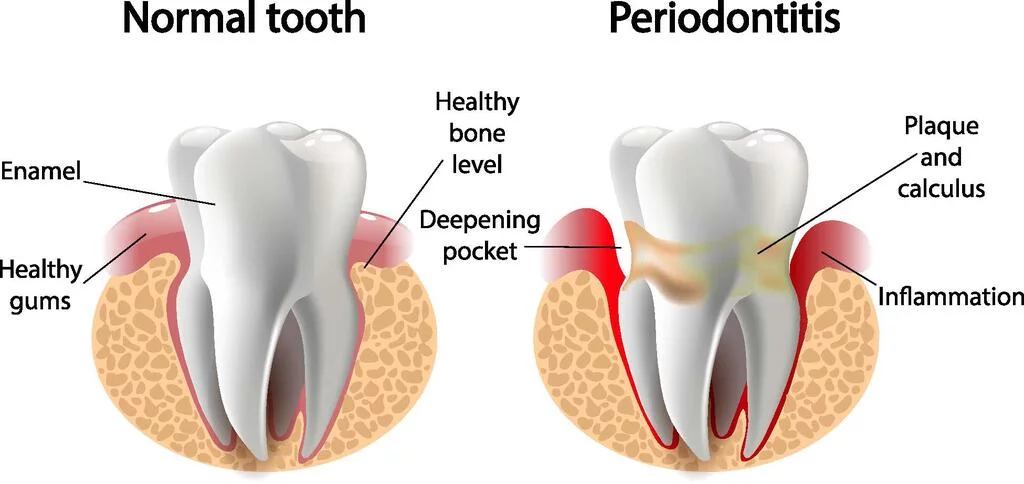
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a gum infection that damages the soft tissue around the teeth. It ranges from mild inflammation to more severe forms that can lead to tooth loss if left untreated. This gum disease has three stages.
Stage One: Gingivitis – This first stage of gum disease is called gingivitis. It is an inflammation of the gums caused by plaque and Calculus buildup on teeth. At this stage, it is reversible if treated.
Stage Two: Periodontitis – If you failed to treat gingivitis which is stage one, it could lead to periodontitis. This Periodontitis infects the gum tissue more seriously than gingivitis. It causes gum pockets and infection of the bone tissue.
Stage Three: Chronic Periodontitis – In this stage of gum disease, the gum pockets formed at stage two now cause the gum tissue to separate from your teeth. This separation can lead to your teeth becoming loose or mobile since no gum is attached to them and thereby falls out.
Recognizing the symptoms of gum disease and taking appropriate action is essential to prevent further complications. In this article, we will explore the common symptoms of gum disease and discuss what steps you can take to address this issue.
What Are the Symptoms of Gum Disease?
If you want to determine a healthy gum by colour then you must have to know that the colour of healthy gums can vary from light pink in some people to dark pink and brown in others. Also, healthy gums are firm and fit very well around teeth. If you experience any of the below symptoms, then it shows that you might have gum disease.
Symptoms of gum disease can include:
Red and Swollen Gums: One of the primary signs of gum disease is redness and swelling of the gums. Healthy gums should have a pale pink colour and feel firm to the touch. However, if you notice that your gums appear redder than usual and feel tender or swollen, it could be an indication of gum disease.
Bleeding Gums: Another common symptom of gum disease is bleeding gums, particularly during brushing or flossing. While occasional minor bleeding can happen due to vigorous brushing, consistent and excessive bleeding is a sign that your gums may be infected or inflamed. If you notice blood on your toothbrush or in the sink after brushing, it’s important to take action.
Persistent Bad Breath: Gum disease is often accompanied by persistent bad breath or a foul taste in the mouth. This occurs due to the bacteria present in the infected gums and pockets around the teeth. If you frequently experience bad breath despite maintaining good oral hygiene practices, it may be a sign of gum disease.
Receding Gums: As gum disease progresses, you may notice that your gums are pulling away or receding from your teeth, leading to the exposure of tooth roots. Receding gums not only affect the aesthetics of your smile but also expose the tooth’s sensitive root surface, making it more prone to sensitivity and decay.
Loose or Shifting Teeth: In the advanced stages of gum disease, you may experience loose teeth or notice that your teeth are shifting. This occurs as the supporting structures of the teeth, including the gums and bone, become weakened and damaged. If you have loose teeth or changes in your bite pattern, it is essential to seek immediate dental attention.
What is the Treatment for Gum Disease?
Seek Professional Treatment: If you suspect gum disease or experience persistent symptoms, it’s important to consult a dental professional. Depending on the severity of the disease, your dentist or hygienist may recommend scaling and root planing (deep cleaning), antimicrobial treatments, gum surgery, or other appropriate procedures to address the underlying issues.
How Can I Prevent Gum Disease?
Gum disease can be prevented and the best way to achieve it is to get into the habit of taking good care of your mouth and teeth.
Practise Good Oral Hygiene: Maintain a consistent oral hygiene routine by brushing your teeth at least twice a day, using a water flosser and flossing daily. Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Consider incorporating an antimicrobial mouthwash into your routine to help reduce bacteria in the mouth.
Visit Your Dentist Regularly: Schedule regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings to monitor your oral health and detect any signs of gum disease at an early stage. Your dentist or hygienist will assess the health of your gums, perform professional cleaning and guide you on maintaining good oral hygiene.
Adopt a Healthy Lifestyle: A healthy lifestyle can positively impact your oral health. Avoid smoking or using tobacco products as they contribute to gum disease. Maintain a balanced diet, limiting sugary foods and beverages that can promote bacterial growth. Stay hydrated and reduce stress, as it can weaken your immune system and make you more susceptible to gum disease.
Conclusion:
Gum disease can have serious consequences for your oral health if left untreated. By recognizing the symptoms and taking proactive steps, you can help prevent further complications and maintain a healthy smile. Practise good oral hygiene, visit your dentist regularly, adopt a healthy lifestyle, and seek professional treatment when necessary. With these, you can effectively manage gum disease and prevent further complications. Remember, early intervention is key, so don’t hesitate to reach out to your dentist if you suspect gum disease or experience persistent symptoms. Prioritise your oral health, and enjoy a healthy and vibrant smile for years to come.